Abstract
With the ubiquity of rolling shutter (RS) cameras, it is becoming increasingly attractive to recover the latent global shutter (GS) video from two consecutive RS frames, which also places a higher demand on realism.
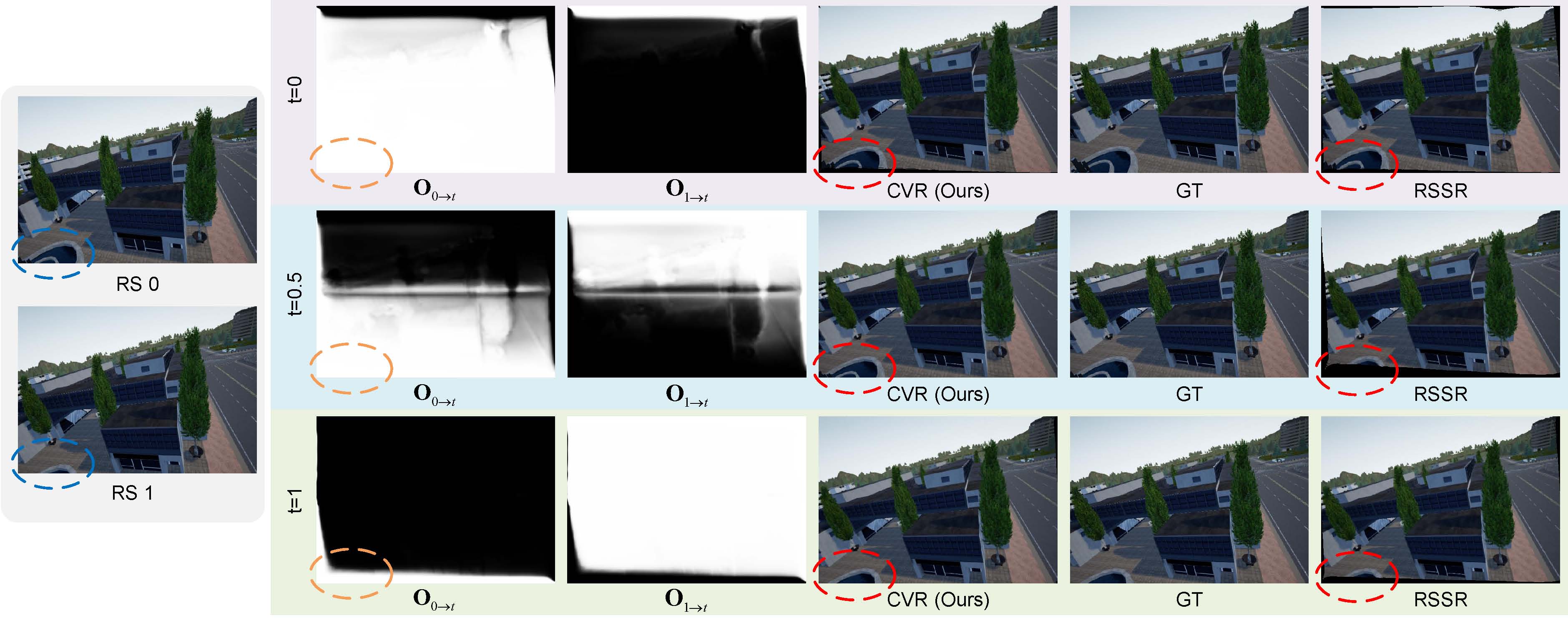
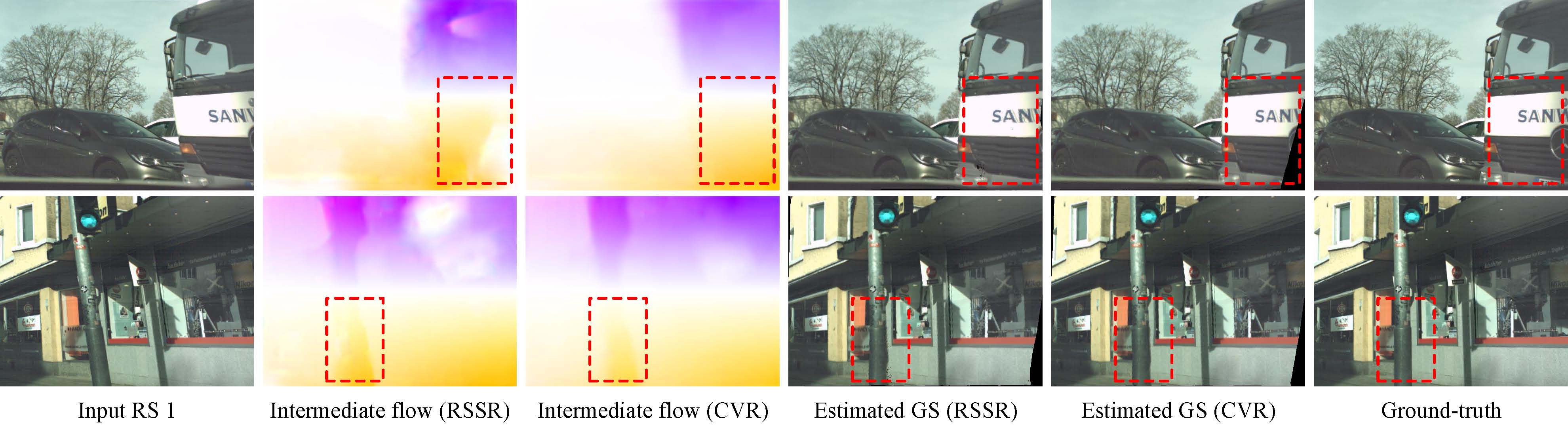
Existing solutions, using deep neural networks or optimization, achieve promising performance. However, these methods generate intermediate GS frames through image warping based on the RS model, which inevitably result in black holes and noticeable motion artifacts.
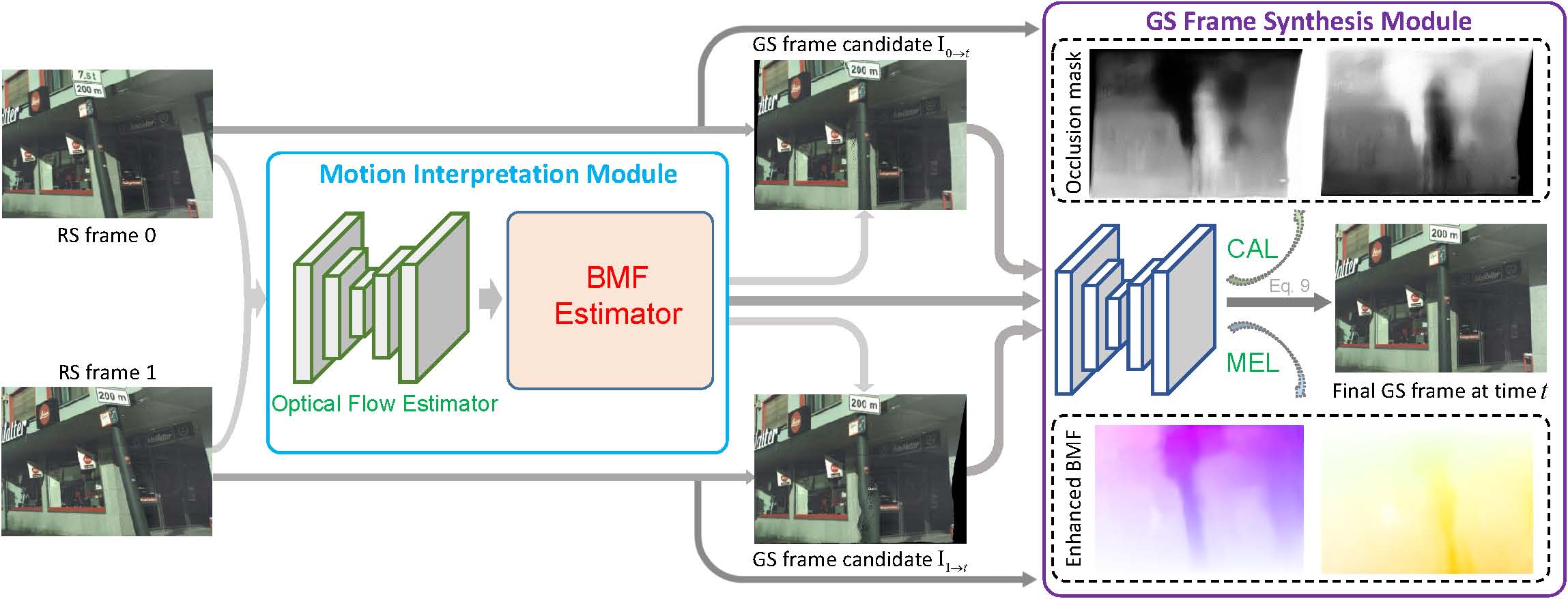
In this paper, we alleviate these issues by proposing a context-aware GS video reconstruction architecture. It facilitates the advantages such as occlusion reasoning, motion compensation, and temporal abstraction.
Specifically, we first estimate the bilateral motion field so that the pixels of the two RS frames are warped to a common GS frame accordingly.
Then, a refinement scheme is proposed to guide the GS frame synthesis along with bilateral occlusion masks to produce high-fidelity GS video frames at arbitrary times.
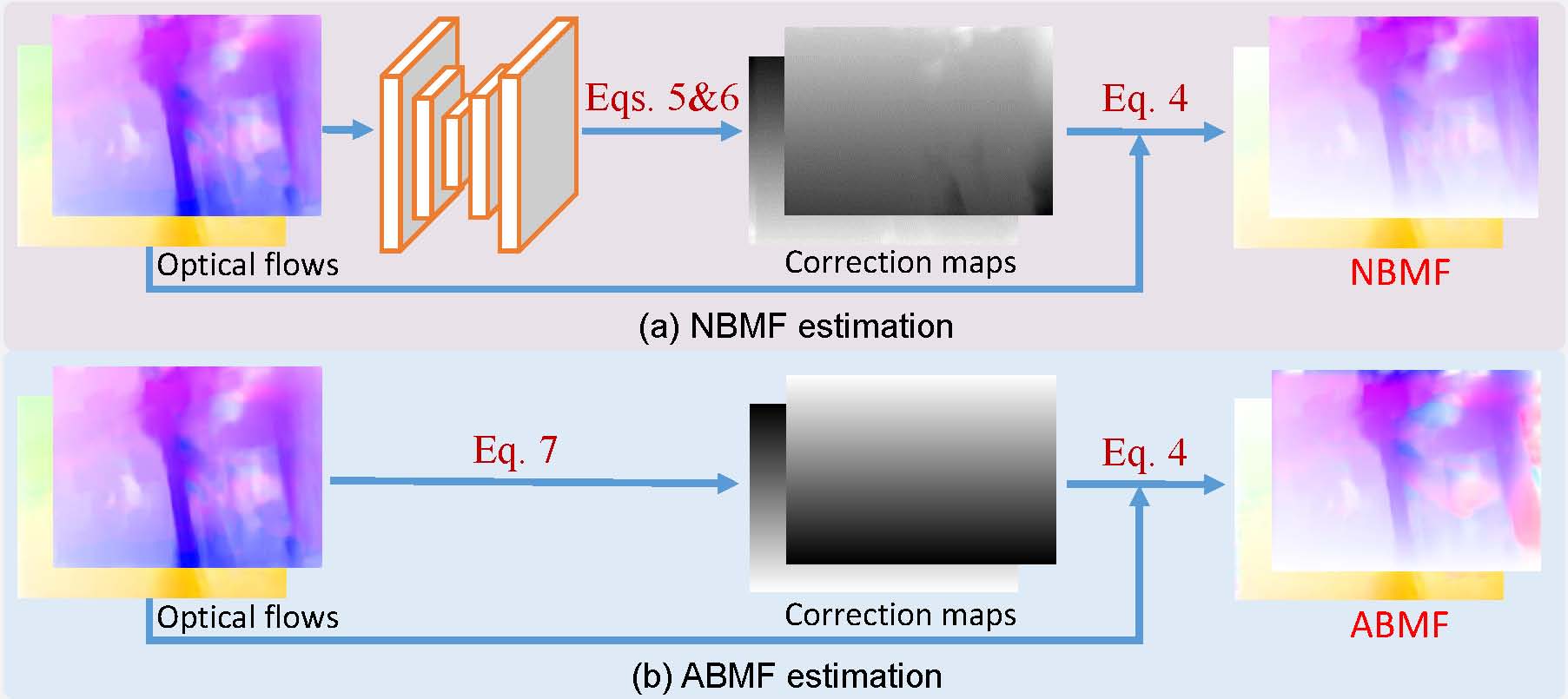
Furthermore, we derive an approximated bilateral motion field model, which can serve as an alternative to provide a simple but effective GS frame initialization for related tasks.
Experiments on synthetic and real data show that our approach achieves superior performance over state-of-the-art methods in terms of objective metrics and subjective visual quality.