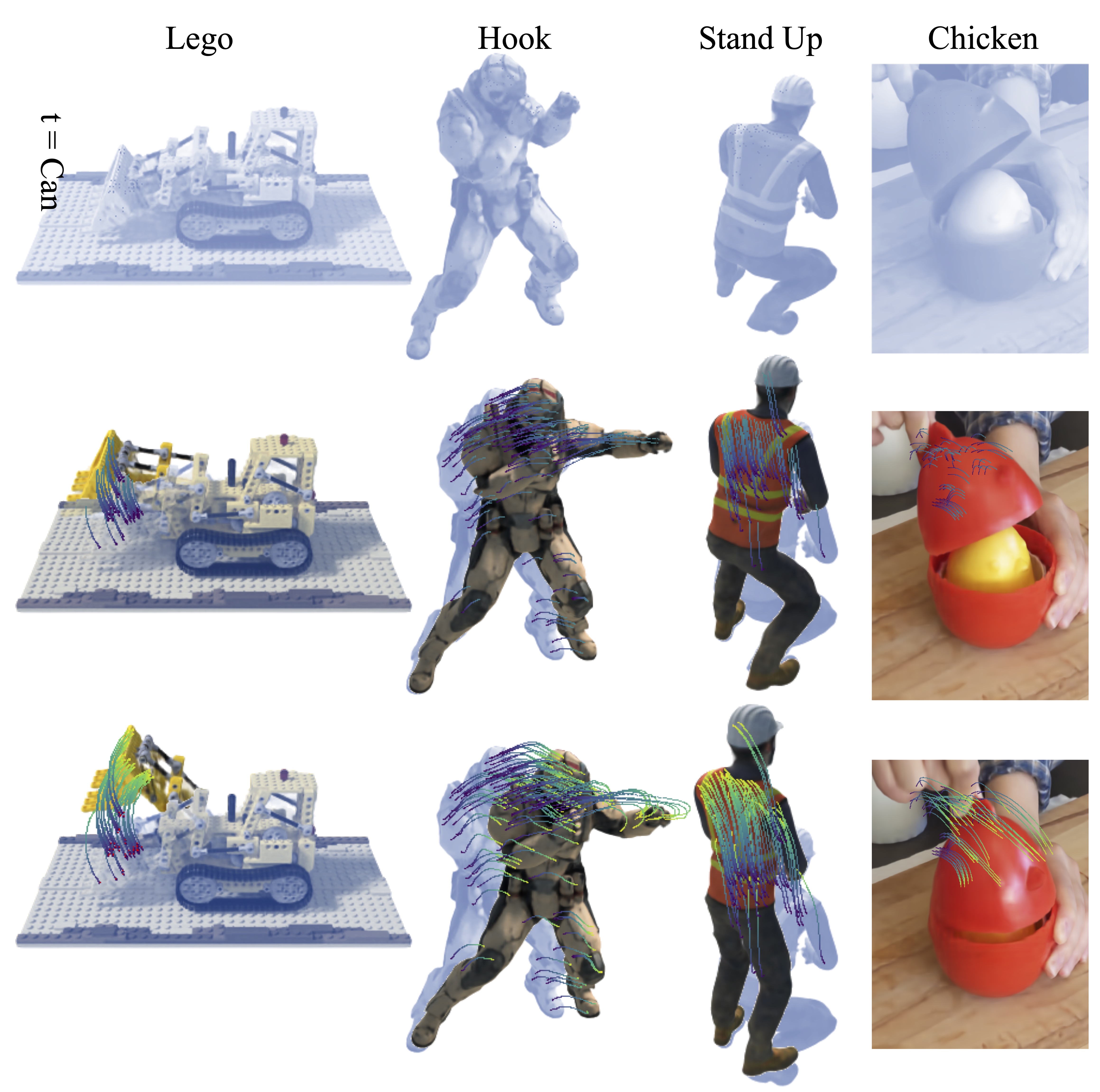
Backward Flow vs Forward Flow
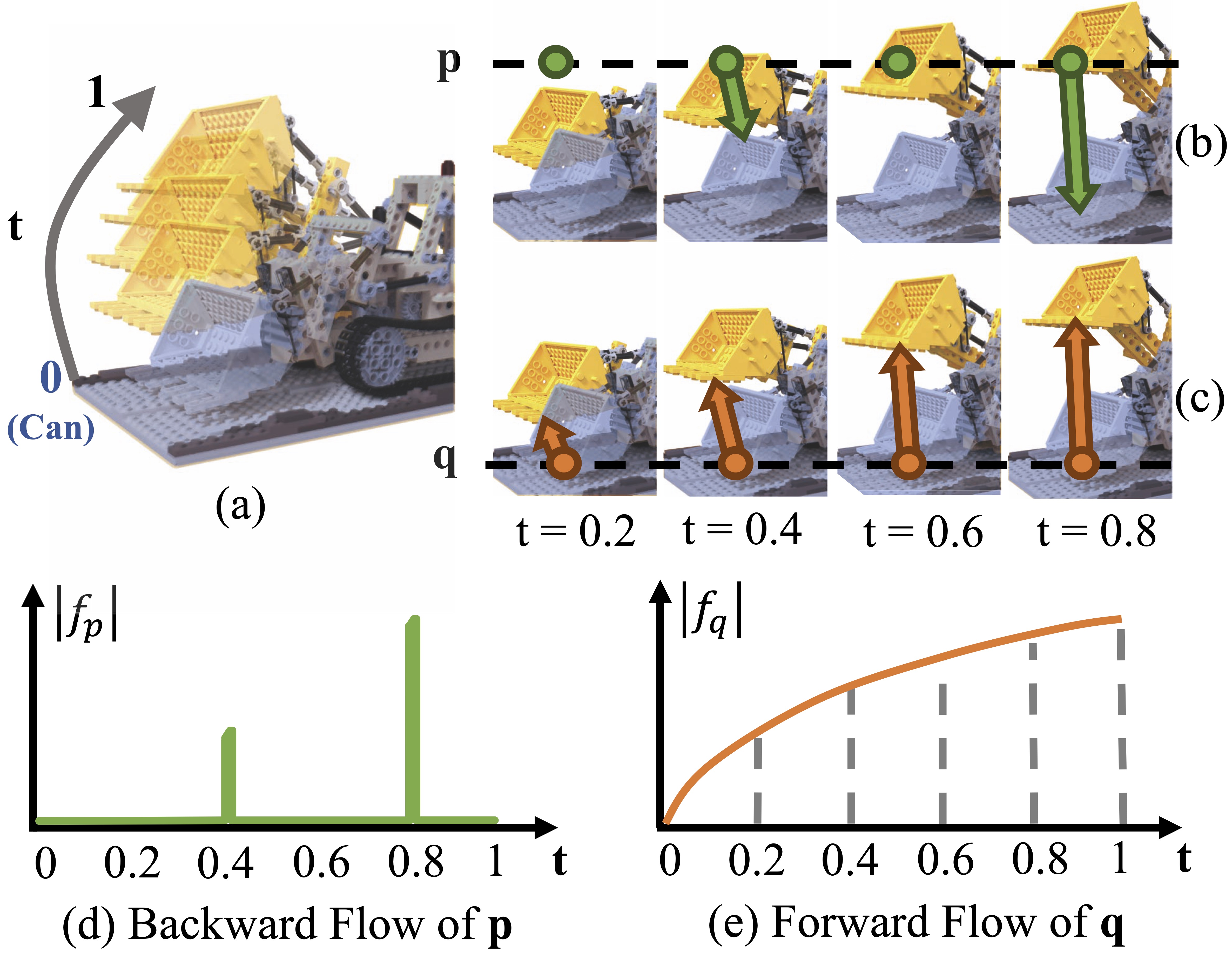
Comparison of backward flow and forward flow. This figure shows an example of backward and forward flow changes. (a) An example of dynamic scene. (b) With the bucket lifting up, different types of points cover the green point $\mathbf{p}$, which needs very different backward flows to map this point back to canonical space. (d) shows the norm changes of the backward flow, which is not smooth. (c) On the other hand, the forward flow of position $\mathbf{q}$, which maps the constant object point from canonical space to other times, is smooth and continuous. (e) shows the norm changes of the forward flow.