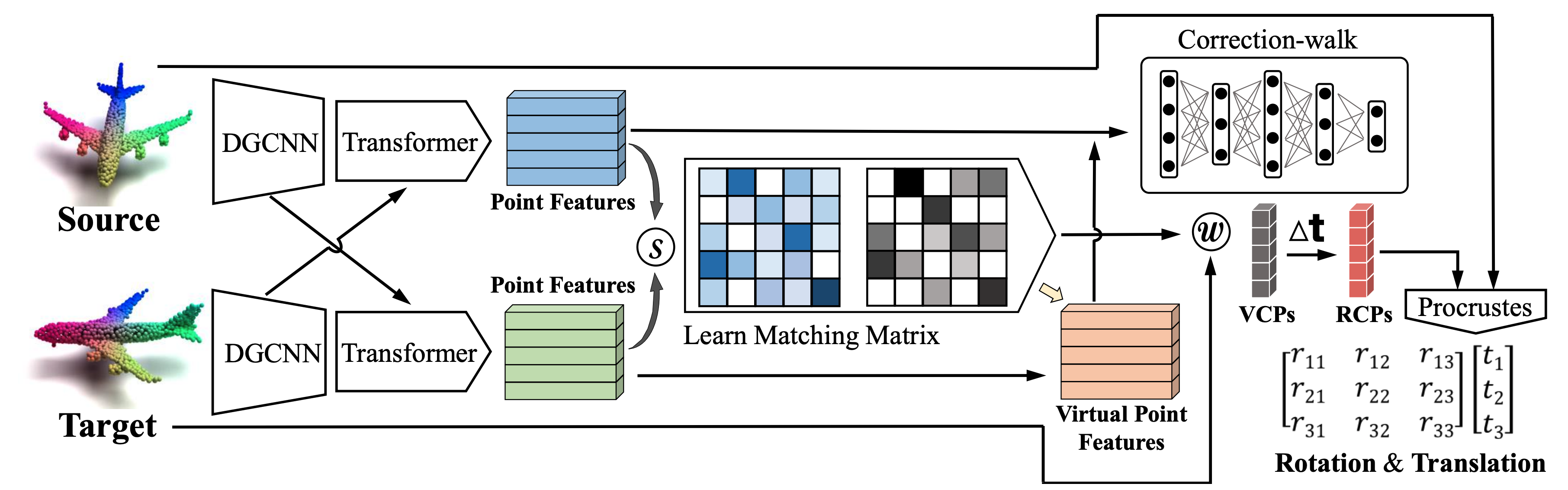
Motivation
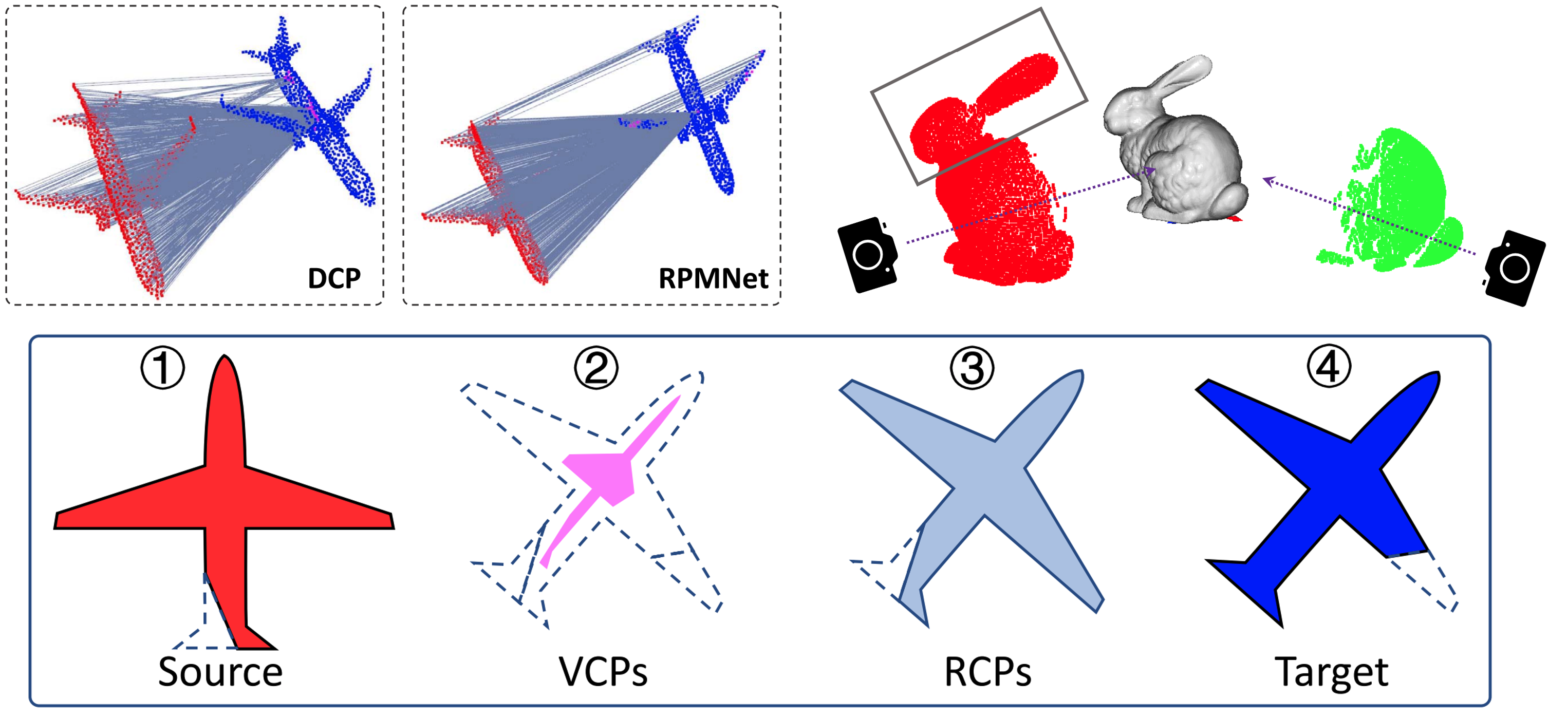
1) The degeneration of the learned corresponding points. Red and blue represent the source and the target respectively. Pink indicates the learned corresponding points. The matching lines connect the source points and the corresponding points. Due to insufficient supervision, the learned corresponding points of DCP and RPMNet degenerate seriously. 2) Illustration of the distribution limitation of VCPs. The red and green represent the source and the target respectively. In this case, only a part of corresponding points can be fitted by the VCPs, which are generated by performing the weighted average on the target. And the corresponding points of the source points marked by the box can never be fitted since the distribution of the VCPs is limited in the convex set of the target. 3) Illustration of our VRNet. ① source and ④ target have different poses and different shapes (broken tail and wing in source and target respectively). The existing methods will learn degenerated VCPs indicated by the pink in ②. Conversely, our VRNet devotes to learning the RCPs indicated by ③, which maintain the same shape as the source and the same pose as the target, by unfolding VCPs and rectifying the partiality of the wing. Hence, the reliable correspondences of these consistent point clouds, i.e. source and RCPs, can be obtained easily since the influence of outliers has been eliminated. Further, the relative pose between source and RCPs can be solved accurately, which is same as the relative pose between source and target.